【論文紹介】構音障害のリハビリテーション効果
はじめに
今回は構音障害のシステマティックレビューの紹介です。
ASHAでも紹介されていたので一見の価値はあるかと思います。
結論としては『交互反復とMPTは改善する』ようですね。
ちなみに、以前にガイドラインにどんなふうに載っているかを記事にしていますので是非。

構音障害のリハビリテーションの効果
今回紹介するのは、『Dysarthria and stroke. The effectiveness of speech rehabilitation. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the studies』です。
どうやらヨーロッパのリハビリジャーナルのようですね。
最初の方にはどんな単語でどんなサイトで検索したかなどの方法が書かれています。
The search was performed using several following medical electronic databases: (1) PubMed, (2)EMBASE, (3) Cochrane Library, and (4) Scopus Web of Science. The review was conducted from15 January to 22 February 2020. We searched for the following terms and keywords: “stroke” and “dysarthria” and “diagnosis” and “stroke” and “dysarthria” and “assessment”.
Chiaramonte, R., & Vecchio, M. Dysarthria and Stroke. The Effectiveness of Speech Rehabilitation. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Studies. European Journal of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine. June 15, 2020
今回は『stroke』、『dysarthria』、『diagnose』、『assessment』で検索したみたいです。
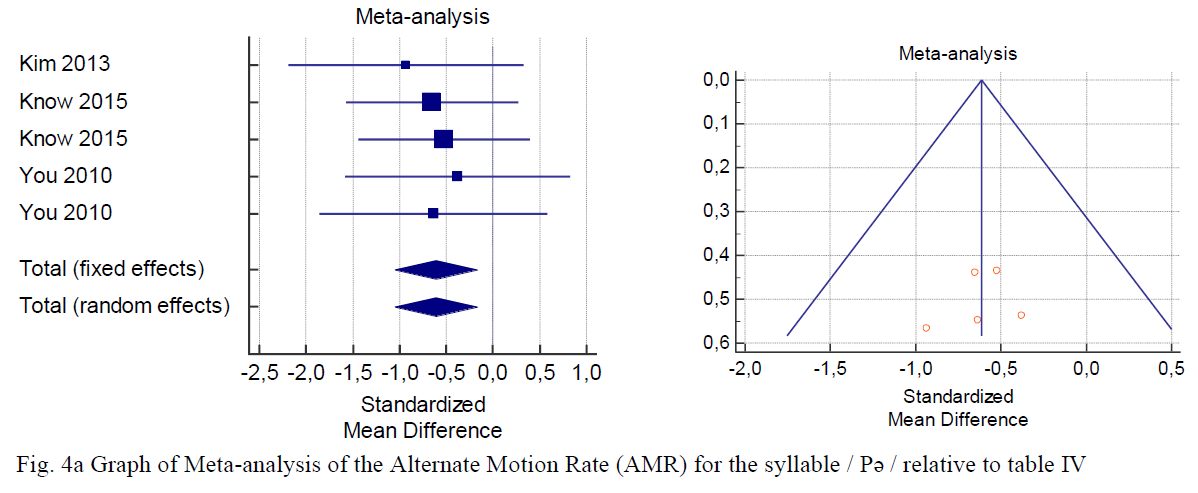
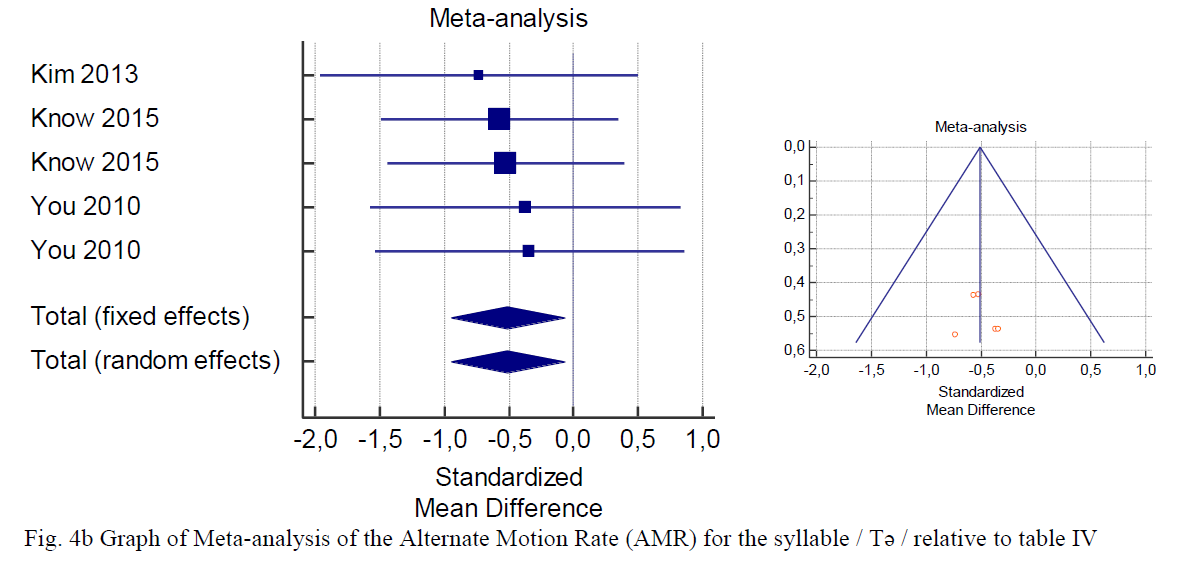
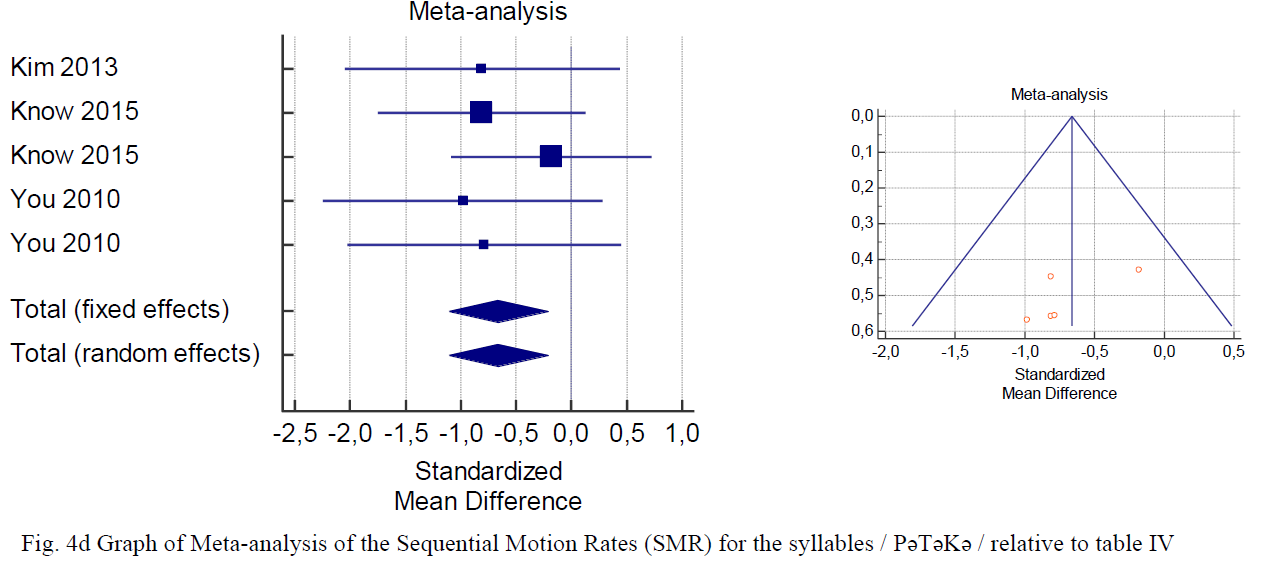
Data pooling within the meta-analysis revealed that several voice and speech parameters, including VSA (table II) (fig. 2) and formants F1 and F2 /a/, /i/, /u/ (Table III and Fig. 3a–f) did not present significant variations before and after treatment (p >0.05).
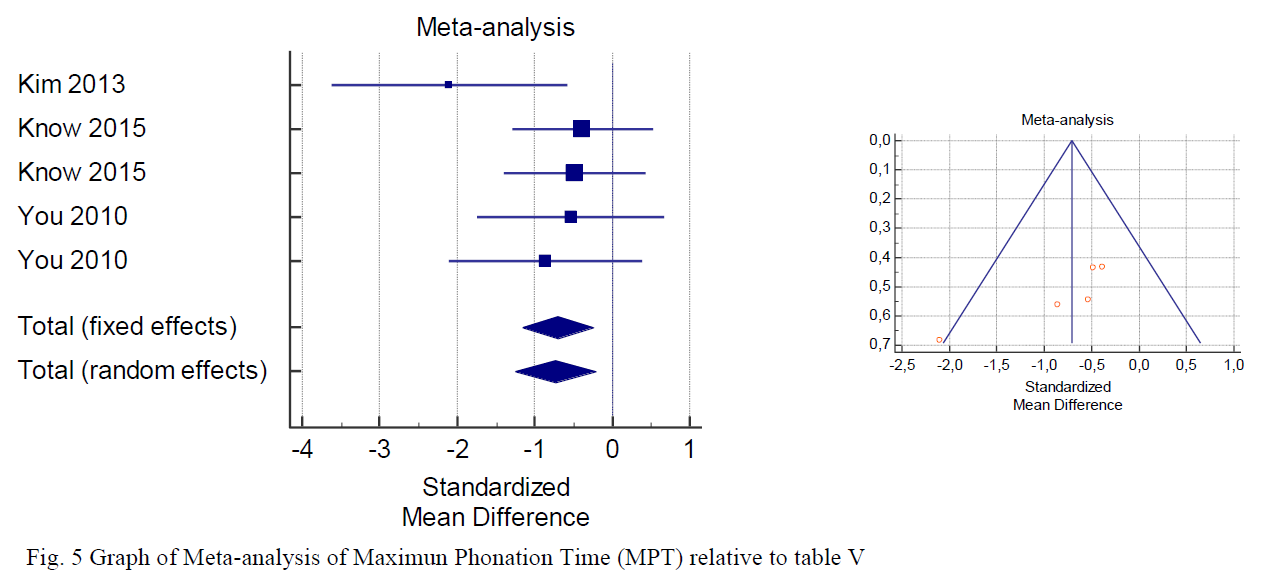
On the contrary, we observed significant variations in AMR- Pə, AMR-Tə, AMR-Kə, and AMRPəTəK (Table IV and Fig. 4a–d) and MPT (Table V and Fig. 5f) before and after treatment. AMR- Pə, AMR-Tə, AMR-Kə, AMR-PəTəK (table IV) and MPT (Table V) significantly discriminated among the severity of stroke-induced dysarthria due and its progression at the end of the speech therapy. These parameters were significantly improved (p <0.05) after speech rehabilitative treatment. Thus, AMR and MPT could be used to obtain significant results to quantify the stroke-related dysarthria severity and during the follow-up examinations.
Chiaramonte, R., & Vecchio, M. Dysarthria and Stroke. The Effectiveness of Speech Rehabilitation. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Studies. European Journal of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine. June 15, 2020
交互反復の「ぱ」、「た」「か」、「ぱたか」とMPTは言語リハビリテーションで有意に効果があったようです。後半に書かれているように、脳卒中に起因する構音障害の重症度を定量化をフォローアップするにも有効ではないかと書かれています。
ただ、数としては決して多いようには見えないのでどこまでこの情報を利用するかは吟味が必要ですね…。
まとめ
音声リハビリテーションを行うことで交互反復とMPTは改善するという論文でした。
リハビリの指標に用いれる可能性があるので参考になりますね。
標準化されている検査でも交互反復はあったと思うので、他項目との経過を確認していく必要がありますね。
何より大切なのは、こうやって分析するためにみんなで症例を論文にまとめることですね。
臨床を形にして積み重ねるしかないので、一致団結してやる必要がありますね。
これからも色々な視点から考えていきたいですね。
皆さんも気づいたことがあればコメントやコンタクトで意見ください。





コメント